
Third-party Cookies: The Hidden Spies in Your Online Activity
In today’s interconnected world, third-party cookies stealthily collect our digital footprints, painting a detailed picture of our online activities. These tiny trackers, often embedded in websites without our explicit consent, monitor our browsing habits and predict our future behavior. While third-party cookies can enhance our online experience by tailoring advertisements and content to our preferences, they raise significant privacy concerns.
HTTP Headers: The Envelope of Web Communication
To understand the role of third-party cookies, we need to delve into the world of HTTP headers. HTTP headers are like envelopes that carry information between a web browser and a web server. When we visit a website, our browser sends an HTTP request to the server, and the server responds with an HTTP response. These headers contain various pieces of information, including cookies.
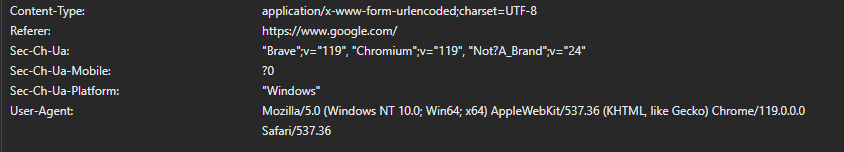
What are Cookies?
Cookies are small text files stored on our devices by websites we visit. They serve as digital breadcrumbs, allowing websites to remember our preferences, login status, and other information for subsequent visits. This can make our online experience more convenient, saving us from repeatedly entering the same information.
Where does the browser store cookies?
Our browsers typically store cookies in temporary or persistent storage. Temporary cookies, also called session cookies, get deleted when we close our browser. On the other hand, persistent cookies stay on our device until they expire or we manually remove them.
Here are the typical locations:
Windows
- Google Chrome:
C:\Users\{Username}\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Cookies - Mozilla Firefox:
C:\Users\{Username}\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\{ProfileName}\cookies.sqlite - Microsoft Edge:
C:\Users\{Username}\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Edge\User Data\Default\Cookies
macOS
- Google Chrome:
~/Library/Application Support/Google/Chrome/Default/Cookies - Mozilla Firefox:
~/Library/Application Support/Firefox/Profiles/{ProfileName}/cookies.sqlite - Safari:
~/Library/Cookies/Cookies.binarycookies
Linux
- Google Chrome:
~/.config/google-chrome/Default/Cookies - Mozilla Firefox:
~/.mozilla/firefox/{ProfileName}/cookies.sqlite
Cookie Security: Protecting Our Digital Identity
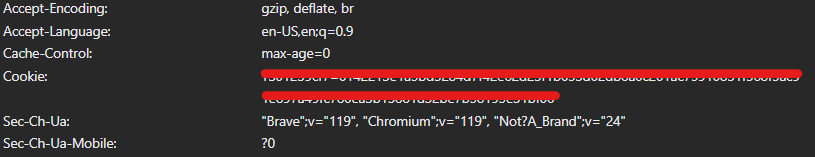
Online privacy can be tampered if the cookies falls into the wrong hands. Malicious actors can hijack cookies to gain unauthorized access to our accounts, steal personal information, or inject malware onto our devices. It is essential to protect our cookies by enabling cookie encryption and regularly deleting unnecessary cookies.
The Dance of Cookies Between Client and Server
When we visit a website, our browser sends an HTTP request to the server. If the website uses cookies, the server includes these cookies in the HTTP response. Our browser stores these cookies, and on subsequent visits, it sends them back to the server along with each HTTP request. This allows the website to recognize us and provide a personalized experience.
First-party Cookies vs. Third-party Cookies: Understanding the Difference
First-party cookies are placed by the website you are currently visiting. They serve to maintain user sessions, retain preferences, and deliver a customized experience. Third-party cookies, on the other hand, are deployed by websites other than the one you are currently visiting. Their primary function is for advertising, tracking, and analytics purposes.
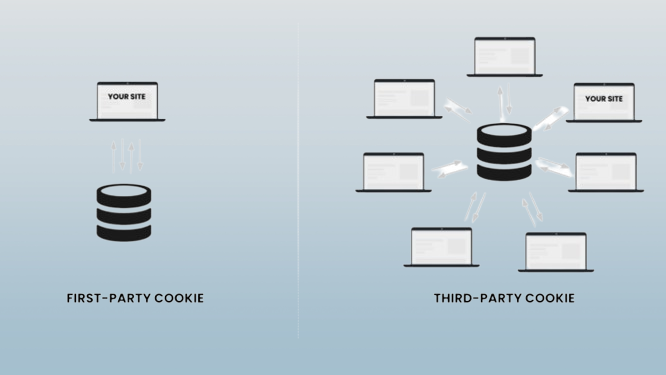
The Pervasive Presence of Third-party Cookies
Third-party cookies are ubiquitous in the online world, embedded in countless websites and applications. They are the brainchild of advertisers and data analytics companies, who use them to track user behavior across the web. These cookies are designed to be inconspicuous, operating silently in the background without our direct knowledge.
How Third-party Cookies Work: Unraveling the Mechanism
When you visit a website, your browser forwards a request to the website’s server. The server replies by sending the requested content along with additional data, which includes third-party cookies. These cookies get placed on your device, either temporarily or permanently, depending on their settings.
Once a third-party cookie lodges itself onto your device, it activates whenever you visit a website containing a script or tag from the same domain. The cookie gathers information about your visit, such as the pages you view, the links you click, and the products you consider. This data is then transmitted back to the third-party server, where it gets utilized to construct detailed profiles of your online behavior.
Here is an example of how this works:
- You visit a website that sells shoes.
- The website sets a third-party cookie on your device.
- You visit another website that also sells shoes.
- The activated third-party cookie gathers information about your visit to this website.
- The website then sends this information back to its original source, where it constructs a profile based on your shoe-buying habits.
Login Fingerprinting: The Stealthy Tracking Technique
Login fingerprinting is a technique that uses non-cookie data, such as browser configuration, device type, and time zone, to create a unique profile of a user. This profile can be used to track users across different websites, even if they have blocked third-party cookies.
Shielding Yourself from Third-party Cookies: Steps to Block and Manage
Fortunately, we have the power to control how third-party cookies track our online activities. Most browsers offer built-in settings to block or limit third-party cookies. Additionally, various extensions and privacy-focused browsers provide enhanced protection against tracking, which keeps our online privacy safe and secure.
Blocking Third-party Cookies in Different Browsers:
- Google Chrome: Go to Settings > Privacy and Security > Cookies and other site data and choose “Block third-party cookies.”
- Mozilla Firefox: Go to Options > Privacy & Security and check the box next to “Block third-party cookies and site data.”
- Microsoft Edge: Go to Settings > Privacy, search, and services > Cookies and select “Block third-party cookies.”
- Apple Safari: Go to Preferences > Privacy and check the box next to “Prevent cross-site tracking.”
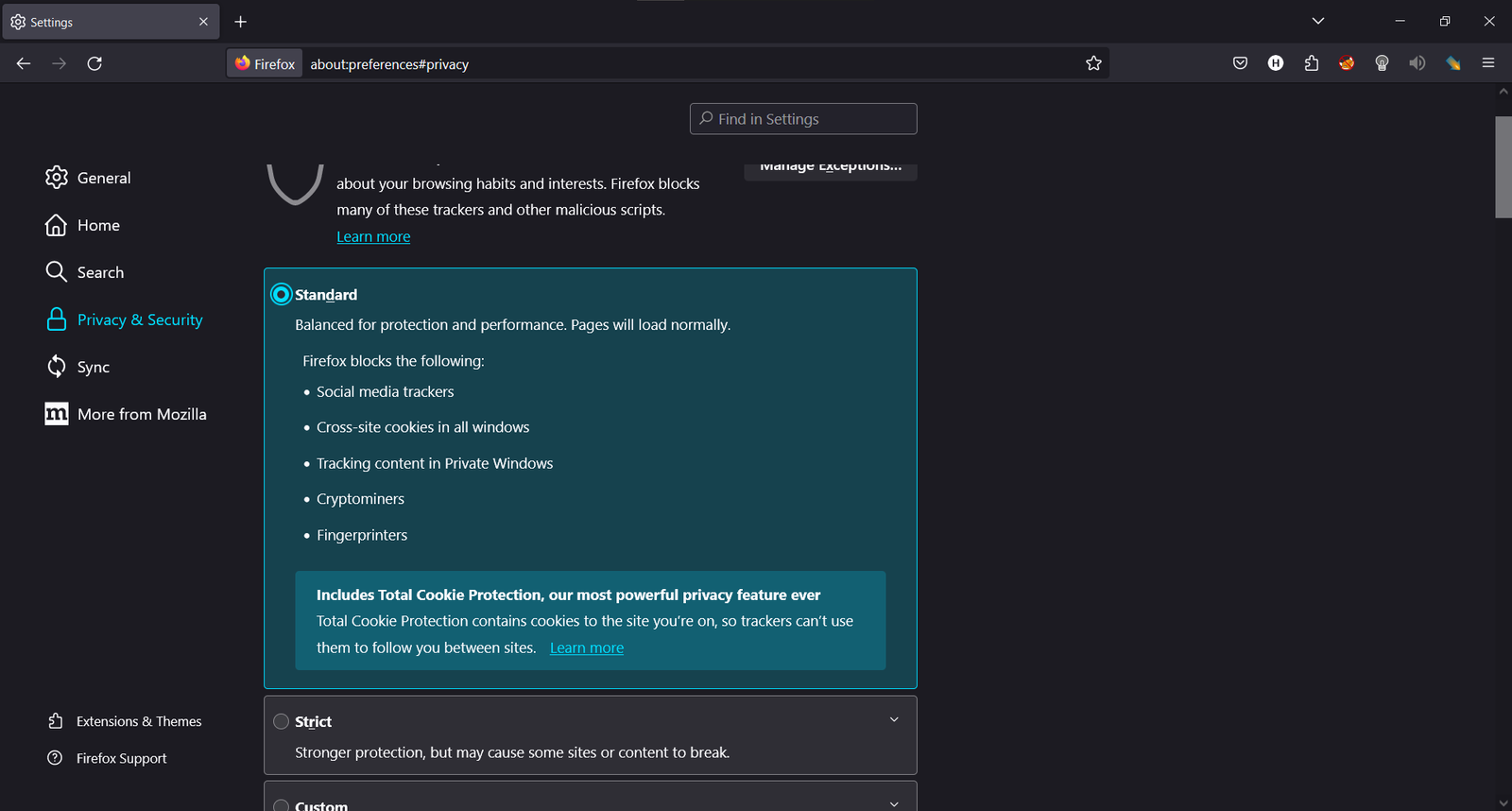
Taking Control of Our Digital Privacy: Strategies to Counter Tracking
Fortunately, we have the power to control how third-party cookies track our online activities. Various tools and techniques are available to protect our privacy and reduce the amount of data we share with third parties. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
1. Utilize Browser Settings to Block Third-party Cookies: Most web browsers offer built-in settings to block or limit third-party cookies. This is a simple yet effective way to reduce tracking. In Chrome, for instance, you can go to Settings > Privacy and Security > Cookies and other site data and choose “Block third-party cookies.”
2.Empower Your Browsing Experience with Privacy-Focused Extensions: Shield your online privacy with browser extensions like Privacy Badger, DuckDuckGo Privacy Essentials, and uBlock Origin. These extensions act as vigilant guardians, actively blocking trackers and preventing data collection. They intercept requests to third-party servers, severing the flow of tracking data and protecting your digital footprint..
3. Explore Privacy-oriented Browsers: Browsers like Brave, Tor, and DuckDuckGo prioritize privacy and offer built-in protection against tracking. These browsers use various techniques to block trackers, prevent data collection, and enhance user privacy.
4. Consider Switching to Incognito Mode: Incognito mode, also known as private browsing, prevents your browser from storing cookies and browsing history. While it doesn’t make you entirely invisible online, it can be a helpful temporary measure to reduce tracking.
Conclusion:
Third-party cookies, while often unseen, play a significant role in our online experience. They can personalize our interactions but also raise concerns about privacy and data ownership. By taking control of our browser settings, adopting privacy-enhancing tools, and making informed choices about our online behavior, we can reclaim our digital privacy and navigate the online world with greater peace of mind.
Remember, your digital privacy is your right. Take control of your online experience and safeguard your personal information. By following these simple yet effective steps, you can minimize the impact of third-party cookies and protect your privacy in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Additional resources:
- What are cookies?: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cookie
- How to block cookies: https://support.google.com/accounts/answer/61416?hl=en&co=GENIE.Platform%3DDesktop
- Alternatives to cookies: https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2022/feb/02/techscape-google-chrome-cookies



