Emerging Cyber Threats
The threat of cyber attacks is growing as we become more dependent on technology and the internet. Emerging cyber threats are constantly evolving, becoming more sophisticated and unpredictable, making it increasingly difficult to protect our digital assets. It’s essential for individuals and businesses to remain aware of the latest trends and take steps to mitigate risks.
In this blog, I’ll discuss some of the most prominent emerging cyber threats, including
ransomware, phishing attacks, Internet of Things (IoT) security, and cloud security. I’ll provide real-life examples of each threat and share practical advice on how to protect yourself.
Ransomware Attacks
These attacks are one of the most devastating types of cyber attacks. Ransomware is a form of malware that encrypts your files and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key. These attacks can cause significant damage to individuals and businesses, often resulting in data loss or theft.
Moreover, in recent years attackers have increased their sophistication and are employing new tactics like double extortion, wherein they first steal the data and then encrypt it to demand ransom.
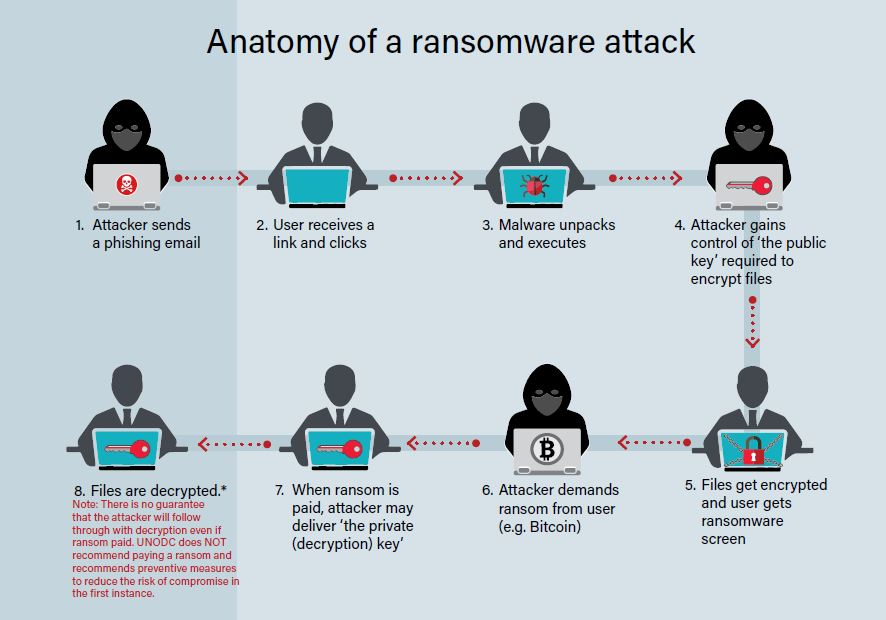
Real-life-Example
A ransomware attack in 2021 targeted the Colonial Pipeline, a major fuel pipeline in the United States, resulting in widespread fuel shortages and panic buying across several states.
Protection against ransomware threats
To protect yourself from ransomware attacks, ensure that you have proper backups of your data and
keep your software up-to-date. Additionally, it is also important to be cautious when opening emails or messages from unknown sources. Regularly scanning your devices and systems for any vulnerabilities can help you detect potential ransomware attacks.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are a type of cyber attack that involves tricking victims into sharing personal information such as
login credentials, credit card numbers, and other sensitive data.
Attackers use various tactics such as emails, texts, or phone calls that seem legitimate to lure their victims into
giving up their data. Phishing attacks are common and pose a significant risk to individuals and businesses alike. Cybercriminals are becoming more skilled in creating convincing fake websites, fake login pages, and even fake invoices that look genuine.

Real-life-Example
In 2021, a phishing attack on the SolarWinds software company led to a major supply chain attack that affected multiple U.S. government agencies and private companies.
Protection against phishing threats
To protect yourself from phishing attacks, always be cautious when clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources. Ensure that you have anti-phishing software installed and keep your software and security tools up-to-date. Be wary of any unsolicited messages, and when in doubt, verify the authenticity of the message’s sender through a trusted channel.
Internet of Things (IoT) Security
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the network of physical devices, vehicles, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, enabling them to connect and exchange data. These devices offer many benefits, but they also present significant security risks. IoT devices can be vulnerable to attacks and can be used to gain access to other parts of a network.

Real-life-Example
A vulnerability was discovered in a popular smart lock system in 2021, which could have enabled attackers to remotely unlock doors without proper credentials. Attackers could have exploited this vulnerability to gain access to homes and businesses.
Protection against IOT threats
To protect yourself from IoT security risks, it’s important to ensure that you change default passwords on IoT devices and keep their software up-to-date. Ensure the security of your home or business network and isolate your IoT devices on a separate network to strengthen their security. Additionally, regularly monitor your devices for unusual activity and disable any unused features or services.
Cloud Security
These has become increasingly popular, but it also presents unique security challenges. Cloud security pertains to the protection of data and applications that are hosted on remote servers.

Real-life-Example
In 2021, a misconfigured cloud server led to a data breach that exposed the personal information of millions of users of a popular mobile app.
Protection against cloud security threats
To protect yourself from cloud security risks, it’s important to choose reputable cloud providers, use strong passwords, and enable multi-factor authentication. You should also regularly monitor your cloud accounts for unusual activity and encrypt your sensitive data.
Insider threats
Insider threats refer to the risk of malicious or unintentional actions by employees or contractors who have access to sensitive information. These individuals can pose a significant threat to the security of an organization, as they have privileged access to sensitive data and systems.

Real-life-Example
In 2013, Edward Snowden, a contractor for the National Security Agency (NSA), leaked classified information about the agency’s surveillance programs to the press. The leak was one of the largest in history and caused significant damage to the reputation of the NSA.
Protection against insider threats
To protect against insider threats, organizations must have policies and procedures in place to manage access to sensitive data and systems. These policies should include regular training for employees and contractors on how to identify and report suspicious behavior. It’s also important to monitor user activity and implement security controls such as access controls, data loss prevention, and user behavior analytics.
Cyber-Physical Attacks
Cyber-physical attacks are a type of cyber attack that targets physical systems or infrastructure,
such as power grids, transportation systems, and industrial control systems.
These attacks can cause real-world damage or disruption, and they are becoming increasingly common as
these systems become more interconnected and reliant on technology.

Real-life-Example
One example of a cyber-physical attack is the Stuxnet worm, which was discovered in 2010. The Stuxnet worm was designed to target industrial control systems used in nuclear facilities in Iran. It was able to cause physical damage to centrifuges used in uranium enrichment by manipulating their operating parameters.
The attack was sophisticated and required a high level of expertise to execute,
and it was widely believed to have been carried out by a nation-state.
Protection against cyber-physical threats
To protect against cyber-physical attacks, organizations need to take a multi-layered approach to security. This includes implementing strong access controls and authentication mechanisms to
limit the ability of attackers to gain access to critical systems. Also, it involves monitoring systems for unusual activity and implementing security controls that can detect and prevent attacks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the examples discussed above illustrate the real-life impact of emerging cyber threats.
As technology continues to advance, it is important for businesses and individuals to stay vigilant
and take steps to protect themselves from these threats.
By staying up-to-date with the latest security trends and best practices,
we can help to minimize the risk of cyber attacks and protect our sensitive data and critical infrastructure.



