
Increased Attacks on Cloud-Based Services: A Growing Concern
In recent years, the adoption of cloud-based services has soared, revolutionizing the way individuals and
organizations store and access their data. The cloud offers unparalleled convenience, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, making it an attractive choice for businesses and individuals alike. However, this surge in cloud usage has also brought about a significant rise in cyber attacks targeting these services. In this blog, we will delve into the escalating threats
faced by cloud-based services, exploring real-life examples of attacks and discussing the importance of robust security measures.
The Basics: Understanding Cloud-Based Services

To fully grasp the magnitude of the problem, it’s crucial to comprehend the fundamentals of cloud-based services.
The cloud allows users to store, manage, and access their data remotely through internet-connected servers,
eliminating the need for local storage infrastructure. This setup enables seamless collaboration, data sharing, and access from any device or location. It also provides various service models, including Software as a Service (SaaS),
Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), catering to diverse user requirements.
Transitioning to the Advanced: Emerging Threats
- Data Breaches: Cloud providers store vast amounts of sensitive data, making them prime targets for malicious actors. Data breaches occur when unauthorized individuals gain access to confidential information, thereby jeopardizing user privacy, financial security, and reputation. Notably, the 2014 breach of the iCloud service exposed
intimate celebrity photos, serving as a stark reminder of the vulnerability of cloud storage. - DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm cloud-based services
by flooding them with massive amounts of traffic, rendering them inaccessible to legitimate users. This technique disrupts operations, hampers productivity, and can result in significant financial losses. In 2016, the DDoS attack
on Dyn, a leading DNS provider, crippled major websites like Twitter, Netflix, and PayPal,
highlighting the far-reaching consequences of such assaults. - Malware Injection: Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in cloud systems to inject malicious code or
malware, allowing them to gain control, steal data, or disrupt services. The “Cloud Hopper” campaign, discovered in 2018, targeted managed IT service providers, infiltrating their networks and compromising clients’ cloud resources. This sophisticated attack affected numerous organizations, emphasizing the significance of robust security measures throughout the cloud ecosystem. - Insider Threats: Cloud services often involve numerous parties, including cloud providers, clients, and third-party vendors. Additionally, insider threats arise when an individual with authorized access misuses their privileges or becomes compromised, leading to unauthorized access, data theft, or other malicious activities. Importantly, the 2020 Capital One breach occurred due to an insider threat, resulting in the compromise of over 100 million customer records.
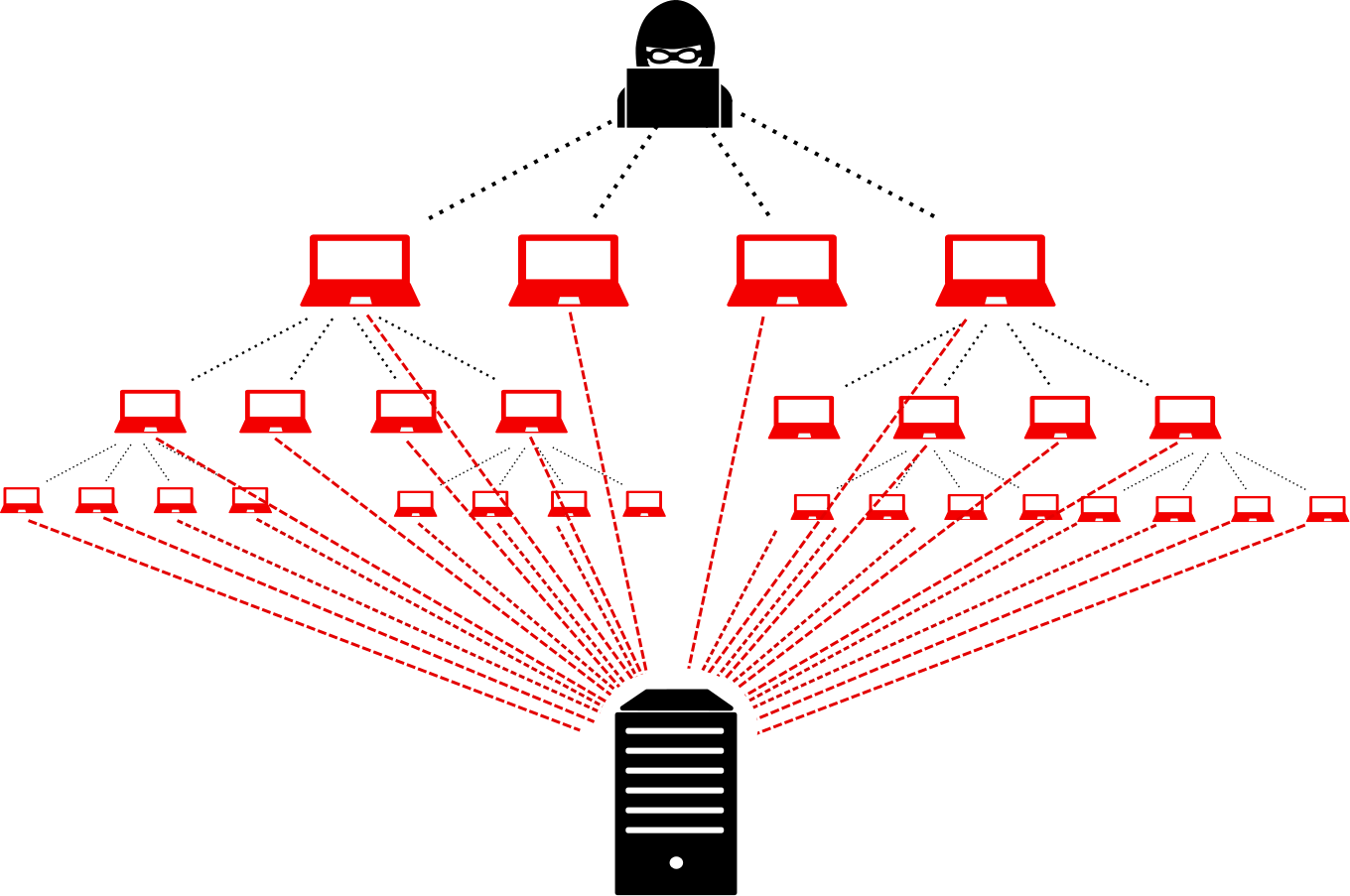
Real-Life Examples of Attacks on Cloud-Based Services
- Target’s Data Breach (2013): In one of the most notable data breaches, retail giant Target fell
victim to a cyber attack that compromised the personal and financial information of approximately 110 million customers. The attackers gained access to Target’s network through a third-party vendor’s credentials, exploiting vulnerabilities in the company’s cloud-based HVAC system. - Dyn DDoS Attack (2016): The Dyn attack, a massive Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, affected numerous major websites and services, including Twitter, Netflix, and PayPal. The attack targeted Dyn’s cloud-based Domain Name System (DNS) infrastructure, causing widespread service disruptions and highlighting the vulnerability of critical cloud-based services.
- Capital One Data Breach (2019): In one of the largest data breaches in banking history, Capital One experienced a breach that exposed personal information of more than 100 million customers. Moreover, the attacker exploited a misconfigured web application firewall (WAF) in Capital One’s cloud environment, thereby gaining unauthorized access to customer data stored on Amazon Web Services (AWS) servers.
- Cloud Hopper Campaign (2018): The Cloud Hopper campaign, attributed to a state-sponsored hacking group, targeted managed IT service providers (MSPs) to gain unauthorized access to their clients’ cloud resources. By infiltrating MSPs’ networks, the attackers gained control over multiple organizations’ cloud environments, allowing them to steal sensitive data and conduct espionage activities.
- Code Spaces Data Deletion (2014): Code Spaces, a code hosting and collaboration platform, faced a devastating attack that led to its permanent shutdown. Attackers gained unauthorized access to the company’s cloud-based infrastructure and started deleting customer data and backups. The attack demonstrated the potential impact of an advanced breach on a cloud service provider, resulting in irreparable damage to the business.

Mitigating Risks: Strengthening Cloud Security
To combat the escalating risks, organizations and individuals must prioritize the implementation of robust security measures within their cloud-based services. Here are some essential steps:
- Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security. This requires users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as passwords, biometrics, or tokens, to gain access. MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and strengthens the overall security posture.
- Encryption: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit is crucial to ensure its confidentiality. This practice transforms data into an unreadable format, making it useless to unauthorized individuals even if they manage to intercept it. By adopting strong encryption algorithms, users can protect their data from unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting periodic security audits helps identify vulnerabilities and ensures compliance with industry standards and best practices. By addressing weaknesses promptly, organizations can proactively mitigate risks and maintain a secure cloud environment.
- Employee Awareness and Training: Educating employees about cloud security best practices is vital to prevent attacks. Training sessions should focus on recognizing phishing attempts, practicing good password hygiene, and understanding the risks associated with cloud-based services. Encouraging a security-conscious culture within the organization can significantly minimize the chances of successful attacks by promoting awareness, fostering a sense of responsibility among employees, and implementing proactive security measures.
Conclusion
As the world increasingly relies on cloud-based services, the threat landscape continues to evolve, necessitating heightened security measures. Organizations and individuals must recognize the potential risks and take proactive steps to safeguard their data and operations. By implementing strong authentication, encryption, conducting regular security audits, and investing in employee training, the risks associated with cloud-based services can be mitigated effectively. Only through a collective effort can we ensure the continued growth and utilization of cloud technology, while simultaneously maintaining the security and integrity of our digital assets.



